Switches & Sensors

ABS Sensor TechnologyThe anti-lock braking system is a safety-critical technology which prevents the wheels from locking and allows the driver to maintain steering control during heavy braking. The four main system components are:
The valve system controls the volume of brake fluid in the brake lines. When the speed sensor detects that a wheel has locked, the hydraulic valve automatically releases brake fluid pressure, thereby releasing the braking pressure. When rotation of the wheel is detected, the pump engages to create pressure and the braking system reapplies the brakes. The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) controls the valves and continually monitors the speed sensor of each wheel. This enables the ECU to evaluate when it needs to override manual braking. ABS, speed or wheel speed sensors, as they are alternatively known, are located on each wheel and as part of the ABS system, they are safety critical components. There are two types of sensor: passive and active. Passive Sensors
Active Sensors The later generation of active sensors are able to register very low speeds, so they are also suitable for traction control and navigation systems. They are digital sensors that work according to the Hall principle and have to be supplied with a current. They usually have three wires: for power supply, earth and a signal. A rotating magnetic element with alternating north/south/north/south polarity in conjunction with a sensor ring creates a digital signal for the ECU – this is how it is able to calculate wheel speed.
Cambiare’s ABS sensor programme is produced in state of the art facilities, conforming to international manufacturing standards including TS16949 and ISO9001 and undergoes stringent tests, pre- and post-production, to ensure it meets the needs of the vehicle application and is of an equivalent standard to the OE part. Overview: Cambiare ABS Sensor Range
|
Related Articles Related Downloads |

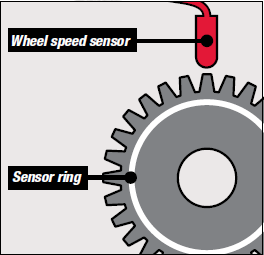 Passive sensors use the principle of variable reluctance to measure the speed of the wheel and operate in a similar way to cam or crank sensors. The sensor, which contains a magnetic pin and copper coil, is mounted with an air gap between it and a metallic toothed ring which rotates at the same speed as the wheel. The alternating teeth and gaps generate a small voltage which is detected by the ECU as wheel speed information. Passive sensors usually have two wires: an earth and a signal wire. They can only register speeds from 3km/hr.
Passive sensors use the principle of variable reluctance to measure the speed of the wheel and operate in a similar way to cam or crank sensors. The sensor, which contains a magnetic pin and copper coil, is mounted with an air gap between it and a metallic toothed ring which rotates at the same speed as the wheel. The alternating teeth and gaps generate a small voltage which is detected by the ECU as wheel speed information. Passive sensors usually have two wires: an earth and a signal wire. They can only register speeds from 3km/hr..png) Active sensors are able to detect when the vehicle is stationary and the direction of a wheel’s rotation. They can also have extra digital inputs for other signals such as brake pad wear monitoring.
Active sensors are able to detect when the vehicle is stationary and the direction of a wheel’s rotation. They can also have extra digital inputs for other signals such as brake pad wear monitoring.